Pharma Brain: Exam Ready iOS and Android App
Transform your pharmaceutical exam preparation with Pharma Brain: Exam Ready!
Designed to revolutionize the way you study, our app offers a dynamic and immersive testing environment focused on equipping you with all the essential knowledge for success in your pharmaceutical exams.
With a broad array of practice questions that span critical topics, we're here to enhance your understanding and boost your confidence.
Key Features:
Extensive Question Bank: Discover an expansive library of practice questions that cover vital areas, ensuring exhaustive preparation for your exams.
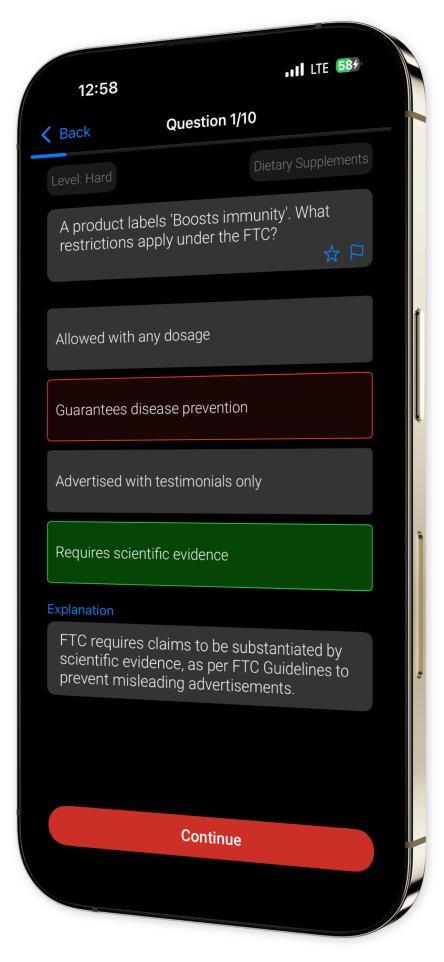
In-Depth Explanations: Benefit from insightful and detailed rationales accompanying each question, nurturing a deeper grasp of pharmaceutical concepts.
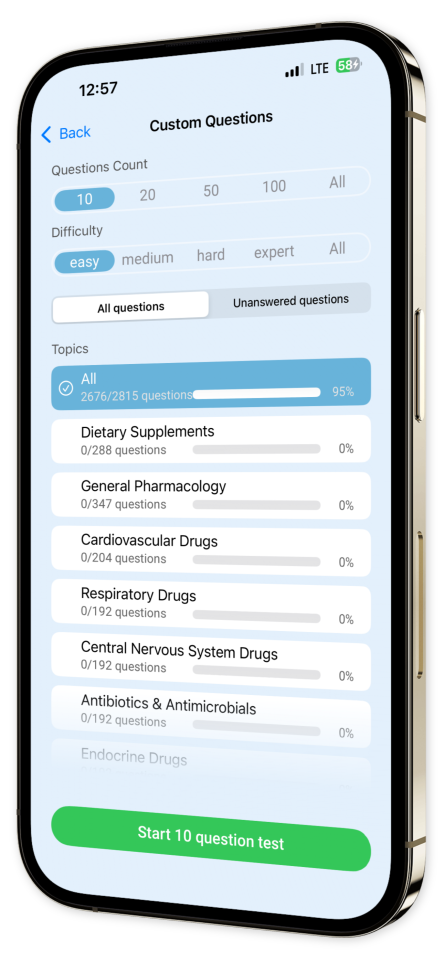
Custom Test Creation: Craft tailor-made quizzes by selecting specific subjects and question types to target your studies on areas demanding more attention.
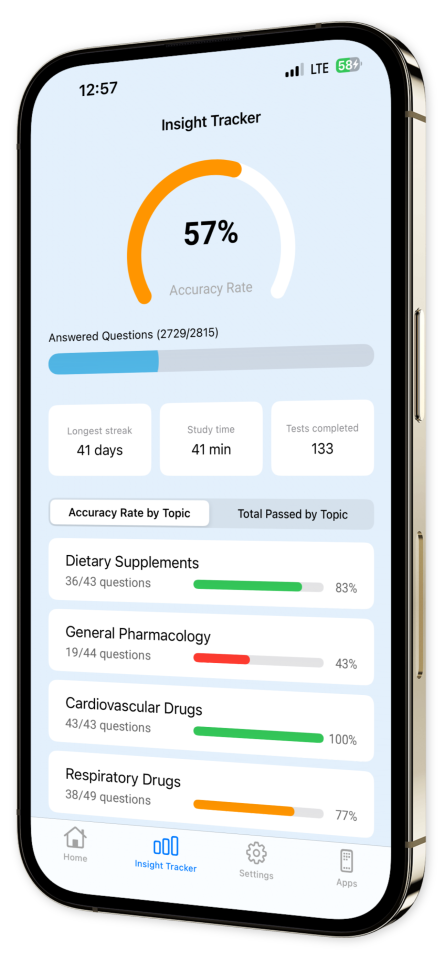
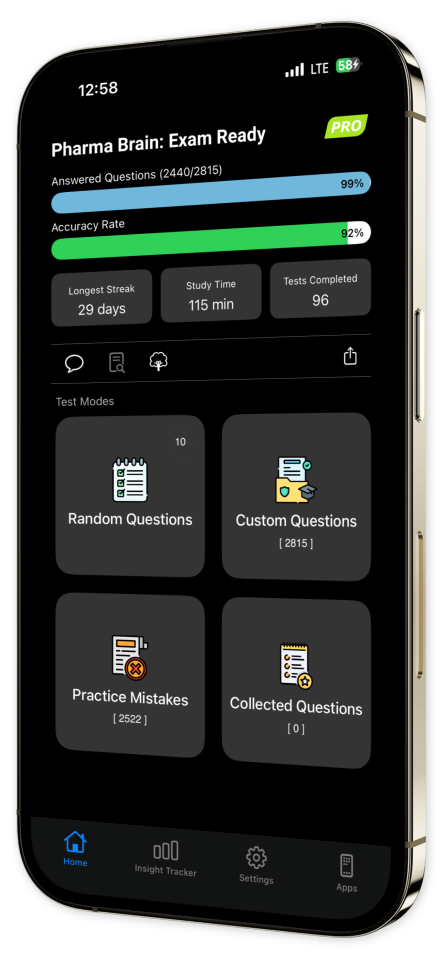
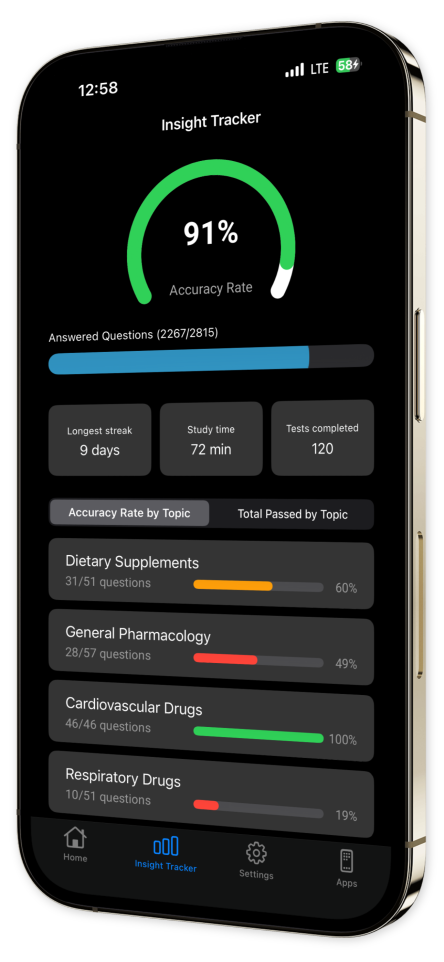
Progress Tracking: Monitor your improvement effortlessly with our sophisticated progress tracking tools, helping you stay on course and achieve your learning goals.
Offline Access: Keep learning uninterrupted with offline access, perfect for maximizing your study time wherever you are, regardless of connectivity.
User-Friendly Interface: Seamlessly navigate through a clean, streamlined design that focuses your cognitive energy on the material without distractions.
Download Pharma Brain: Exam Ready today and embark on a smarter journey towards mastering pharmaceutical knowledge.
Excel in your exams and propel your career to new heights! Make success your companion in the pharmaceutical world with the power of Pharma Brain: Exam Ready at your fingertips.
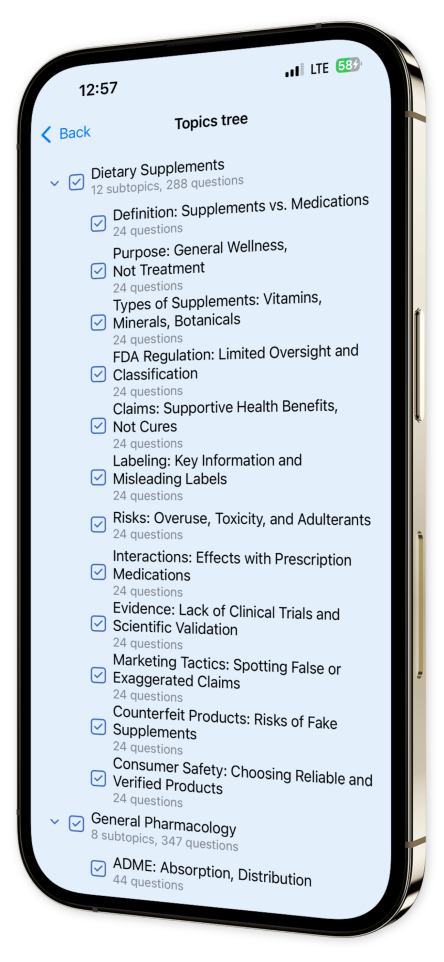
Content Overview
Explore a variety of topics covered in the app.
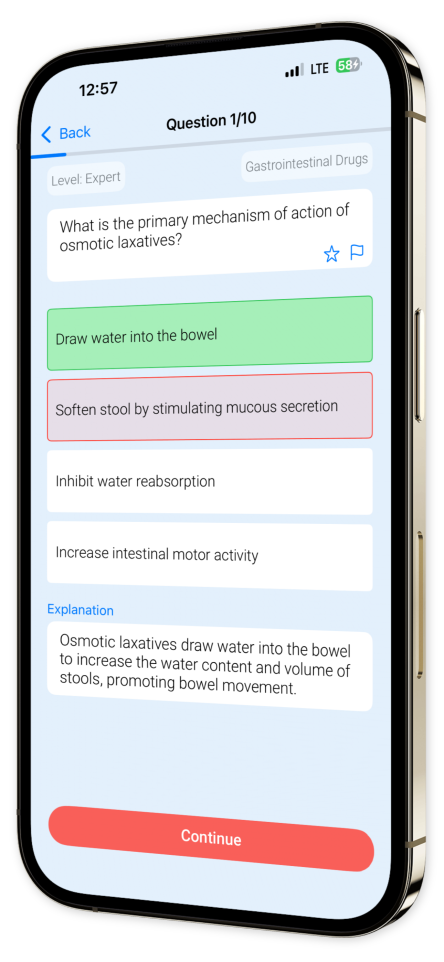
Example questions
Let's look at some sample questions
Which factor significantly impacts oral drug absorption by altering gastric emptying time?
Food intakeDrug pHPlasma protein bindingMetabolic rate
Food intake can slow down gastric emptying time, affecting the rate and extent of drug absorption.
Which factor most influences the volume of distribution of a drug?
Drug ionizationPlasma protein bindingDrug half-lifeExcretion route
Drugs tightly bound to plasma proteins have limited distribution into tissues, resulting in a smaller volume of distribution.
Which Phase II reaction involves adding a glycine molecule?
GlucuronidationAcetylationSulfationAmino acid conjugation
Amino acid conjugation, often with glycine, helps in solubilizing and detoxifying certain drugs, facilitating excretion.
Which enzyme is primarily responsible for phase I oxidation reactions in drug metabolism?
Cytochrome P450GlucuronosyltransferaseGlutathione S-transferaseN-acetyltransferase
Cytochrome P450 enzymes mainly catalyze phase I oxidation reactions, enhancing drug solubility.
A patient has reduced N-acetyltransferase activity. Which drug metabolism phase is mainly affected?
Phase IIPhase IBoth Phase I & IINone
N-acetyltransferase is involved in Phase II conjugation, impacting drug detoxification and solubility.
Which receptor subtype does GABA bind to, resulting in inhibitory effects in the CNS?
GABA-AGABA-BNMDAAMPA
GABA-A receptors are ionotropic receptors in the CNS that mediate inhibitory neurotransmission by allowing chloride ions to enter the neuron.
Nicotine's effects on skeletal muscle are primarily mediated by which receptor type?
Muscarinic receptorNicotinic receptorAlpha-adrenergic receptorBeta-adrenergic receptor
Nicotinic receptors, particularly at neuromuscular junctions, mediate the effects of nicotine on skeletal muscle, not muscarinic or adrenergic receptors.
What effect does an agonist have on a receptor?
Depresses receptor activityBlocks receptor activityActivates receptorsDestroys receptor sites
An agonist binds to a receptor and activates it to produce a biological response.
In treating overdoses, a competitive antagonist might be used to:
Enhance drug actionBind irreversiblyBlock receptor bindingActivate receptors
Competitive antagonists block receptors, counteracting the effects of an overdose by preventing binding of excess agonists.
A drug has an ED50 of 20 mg and a TD50 of 200 mg. Calculate the therapeutic index.
1020155
The therapeutic index (TI) is calculated as TD50/ED50. In this case, TI = 200 mg / 20 mg = 10. Calculation verified: 200 divided by 20 equals 10.